What Causes Increased Heart Rate At Rest
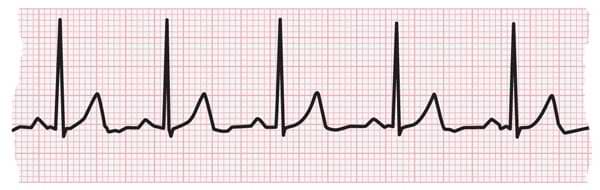
ECG strip showing a normal heartbeat
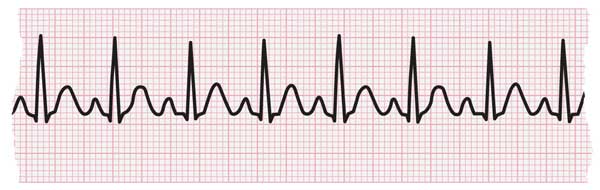
ECG strip showing tachycardia
Tachycardia refers to a heart rate that'south too fast. How that's defined may depend on your age and concrete condition.
More often than not speaking, for adults, a heart rate of more than than 100 beats per minute (BPM) is considered too fast.
View an blitheness of tachycardia.
Types of tachycardias
Atrial or Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
Atrial or supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a fast heart rate that starts in the upper chambers of the heart. Some forms of this particular tachycardia are paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) or paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT).
With atrial or supraventricular tachycardia, electrical signals in the center'due south upper chambers fire abnormally. This interferes with electrical impulses coming from the sinoatrial (SA) node, the center'southward natural pacemaker.
The disruption results in a faster than normal heart charge per unit. This rapid heartbeat keeps the heart's chambers from filling completely between contractions, which compromises claret menses to the balance of the torso.
A profile for atrial or SVT
In full general, those most likely to take atrial or supraventricular tachycardia are:
- Children (SVT is the most mutual type of arrhythmia in kids)
- Women, to a greater degree than men
- Anxious immature people
- People who are physically fatigued
- People who potable big amounts of coffee (or caffeinated substances)
- People who drinkable alcohol heavily
- People who fume heavily
Atrial or SVT is less commonly associated with heart set on or serious mitral valve disease.
Symptoms and complications
Some people with atrial or supraventricular tachycardia may take no discernible symptoms. Others may experience:
- Fainting (syncope)
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Fluttering in the chest
- Bounding pulse
- Breast pressure, tightness or hurting (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
In extreme cases, those suffering with atrial or SVT may likewise experience:
- Unconsciousness
- Cardiac arrest
Treatment for Atrial or SVT
If you have atrial or SVT, it's possible that you won't need handling.
But if the episodes are prolonged, or recur often, your doc may recommend treatment, including:
- Carotid sinus massage: A healthcare professional person tin can apply gentle pressure on the neck, where the carotid artery splits into two branches.
- Pressing gently on the eyeballs with eyes closed. Caution: This procedure should be supervised advisedly by a healthcare doc.
- Valsalva maneuver: This consists of holding your nostrils closed while blowing air through your nose.
- Using the dive reflex: The swoop reflex is the body's response to sudden immersion in water, specially cold water.
- Sedation
- Cut down on coffee or caffeinated substances
- Cutting downward on alcohol
- Quitting tobacco utilize
- Getting more residual
In patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome, medications or ablation may exist needed to control paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT).
Sinus Tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is a normal increase in the heart rate. In this condition, the heart's natural pacemaker, the sinoatrial (SA) node, sends out electric signals faster than usual.
The heart rate is faster than normal, but the heart beats properly.
Causes of sinus tachycardia
A rapid heartbeat may exist your body's response to common conditions such as:
- Anxiety
- Fright
- Severe emotional distress
- Strenuous practise
- Fever
- Some medicinal and street drugs
Other, less common causes may include:
- Anemia
- Increased thyroid activity
- Middle muscle damage from heart set on or centre failure
- Severe haemorrhage
Approach to treatment
Your doctor should consider and treat the crusade of your sinus tachycardia, rather than just treating the status. Simply slowing the heart rate could cause more harm if your rapid heartbeat is a symptom of a more serious or long-term problem.
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia is a fast centre rate that starts in the center's lower chambers (ventricles). This type of arrhythmia may exist either well-tolerated or life-threatening, requiring immediate diagnosis and handling.
The seriousness depends largely on whether other cardiac dysfunction is present and on the degree of the ventricular tachycardia.
Explaining the trouble
In cases of ventricular tachycardia, electric signals in the middle'south lower chambers burn down abnormally. This interferes with electric impulses coming from the sinoatrial (SA) node, the eye'southward natural pacemaker.
The disruption results in a faster than normal heart rate. This rapid heartbeat keeps the middle'due south chambers from filling completely between contractions, which compromises blood catamenia to the residue of the body.
Causes of ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia is most often associated with disorders that interfere with the eye'southward electric conduction organisation. These disorders can include:
- Lack of coronary avenue blood catamenia, depriving oxygen to centre tissue
- Cardiomyopathy distorting the center's structure
- Medication side effects
- Illicit drugs such equally cocaine
- Sarcoidosis (an inflammatory disease affecting skin or body tissues)
Range of symptoms
Symptoms for ventricular tachycardia vary. Common symptoms include:
- Dizziness
- Palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea
- Lightheadedness
- Falling unconscious
- Cardiac arrest, in farthermost cases
Treatment options
The cause of your ventricular tachycardia volition inform your treatment options. Possible approaches include:
- Medication
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Surgery
- Firsthand electrical defibrillation, in extreme cases
Printable Arrhythmia Information Sheets
What Causes Increased Heart Rate At Rest,
Source: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/arrhythmia/about-arrhythmia/tachycardia--fast-heart-rate
Posted by: bishopkinet1945.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Causes Increased Heart Rate At Rest"
Post a Comment